Table des matières
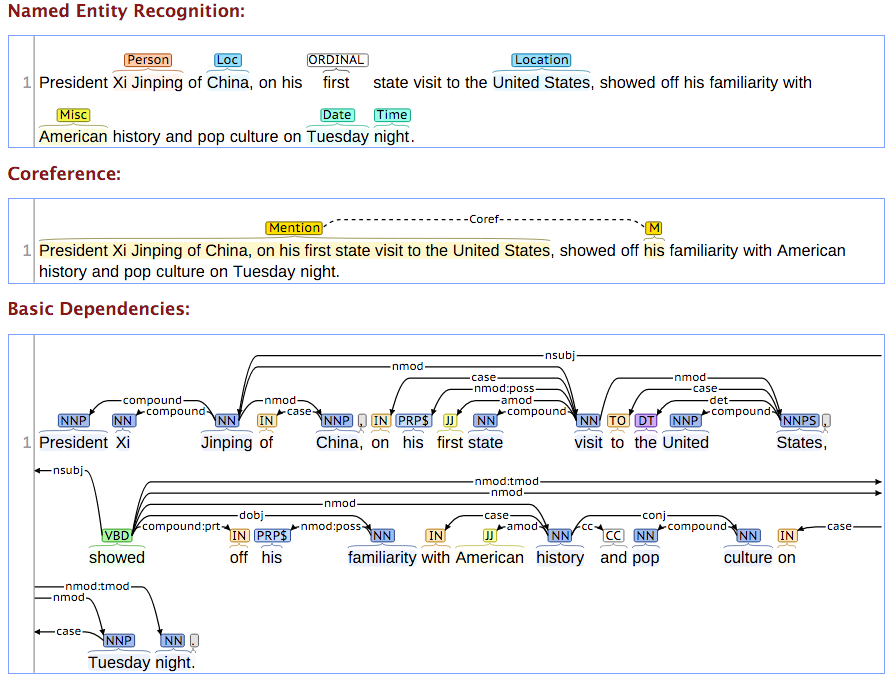
Données massives, apprentissage automatique et éthique
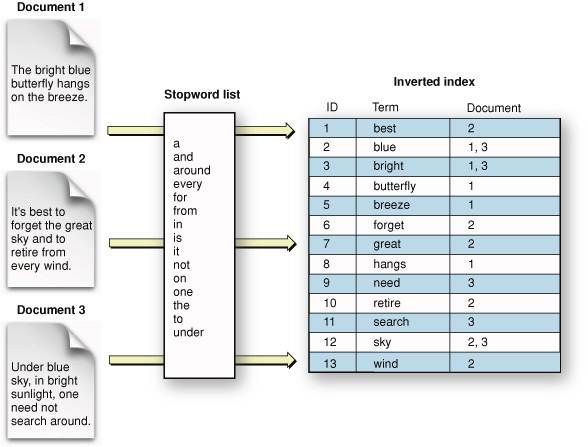
Comment sont entreposées les données massives ?
- SGBDR traditionnels: ne permettent pas de stocker ni d’exploiter efficacement des données massives.
- NoSQL:
- puissance de calcul
- parallélisme
- grappes de calcul.
- Compromis:
- Fusion de sources de données est plus difficile.
- Absence de jointures de tables. - Indexation doit être effectuée par un autre logiciel tel que Lucene
- Référence: (Han et al. 2011; Moniruzzaman and Hossain 2013)
Bases de données analytiques
- Optimisées pour effectuer des calculs statistiques sur des ensembles de données.
- On les appelle parfois bases de données en colonnes.
- La plus connue est Apache HBase
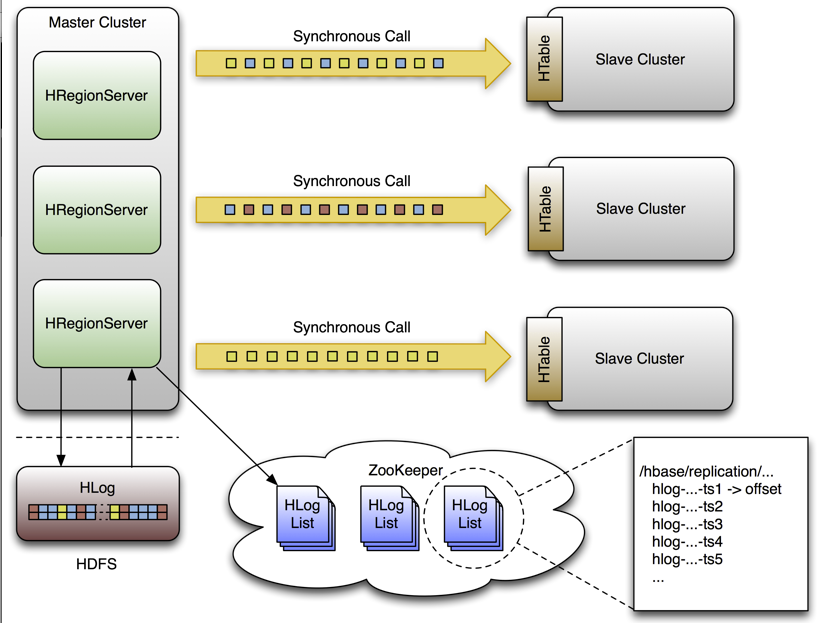 Source - Référence: (Chang et al. 2008)
Source - Référence: (Chang et al. 2008)
Les bases de données de documents
- Permettent d’entreposer toute l’information par rapport à un évènement ou une profil dans un seul enregistrement.
- Pas de schémas au préalable.
- Données faciles à consommer pour une application web.
- La plus connue est MongoDB
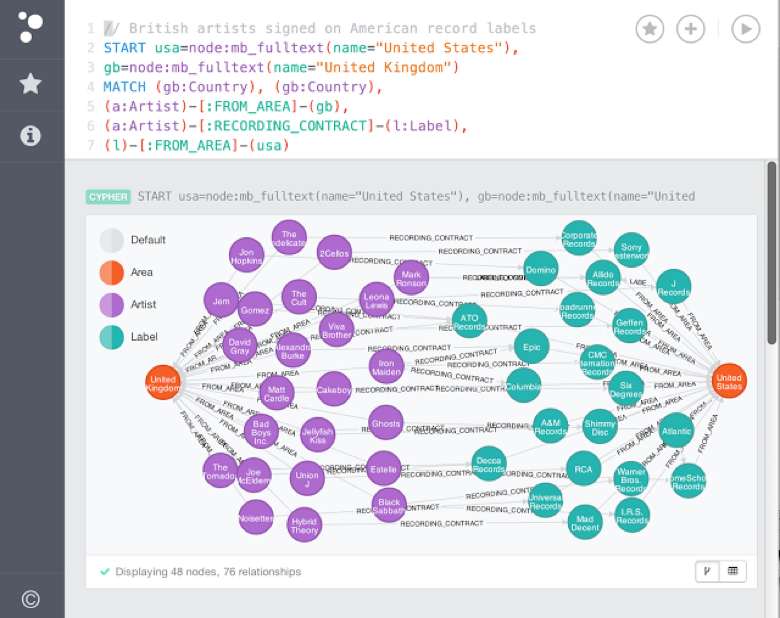
Les graphes
- Deux types de composantes: des noeuds et des arcs.
- Chacunes d’elles possède des étiquettes et des propriétés.
- Représenter des relations entre des entités et des concepts (graphe de propriétés).
- Web sémantique: associer de la connaissance et des capacités de inférence logique aux pages web
- [Angles and Gutierrez (2008); berners2001semantic]
- La plus connue est Neo4j
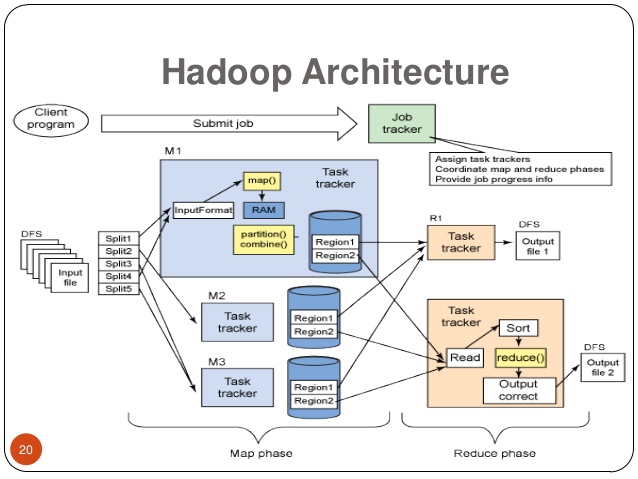
Les lacs de données
- Le lac de données stocke tout type d’information non-structurées:
- journaux applicatifs de serveurs web,
- textes, images, vidéos, voix
- Le plus connu est HDFS, le système de fichiers distribué de Apache Hadoop
On fait quoi de ces données non-structurées?
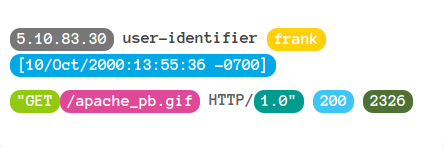
Journaux applicatifs
Utilisation d’expressions régulières. - Par exemple: Logstash
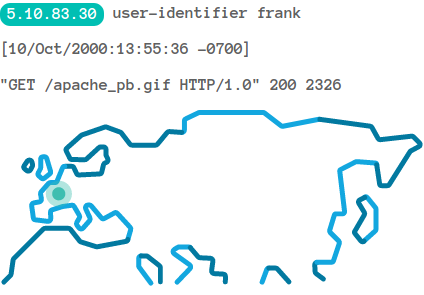
Géo-localisation - Par exemple: Logstash
Textes et voix
Analyse et traitement du langage naturel
- Phonologie, Morphologie, Syntaxe, Sémantique,Raisonnement
- Reconnaissance d’entités (Manning et al. 2014).
- Par exemple: Stanford CoreNLP
Encodage
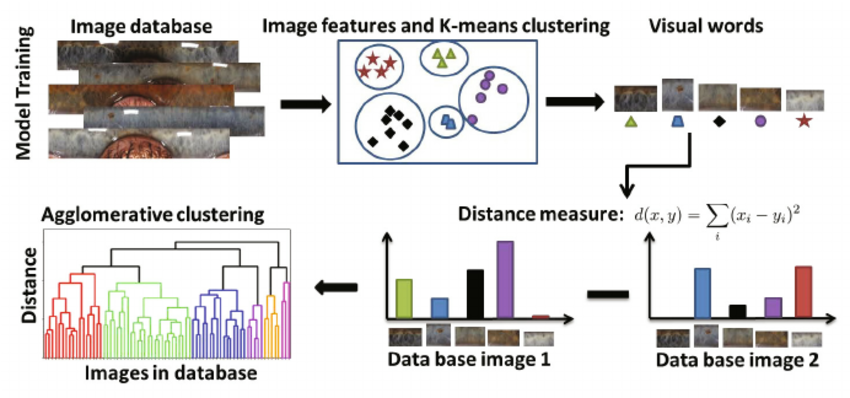
Images et vidéos
Filtres convolutionnels
Palettes de couleurs
Identification d’objets
Description textuelle
 Source (Vinyals et al. 2017; Sivic and Zisserman 2009)
Source (Vinyals et al. 2017; Sivic and Zisserman 2009)
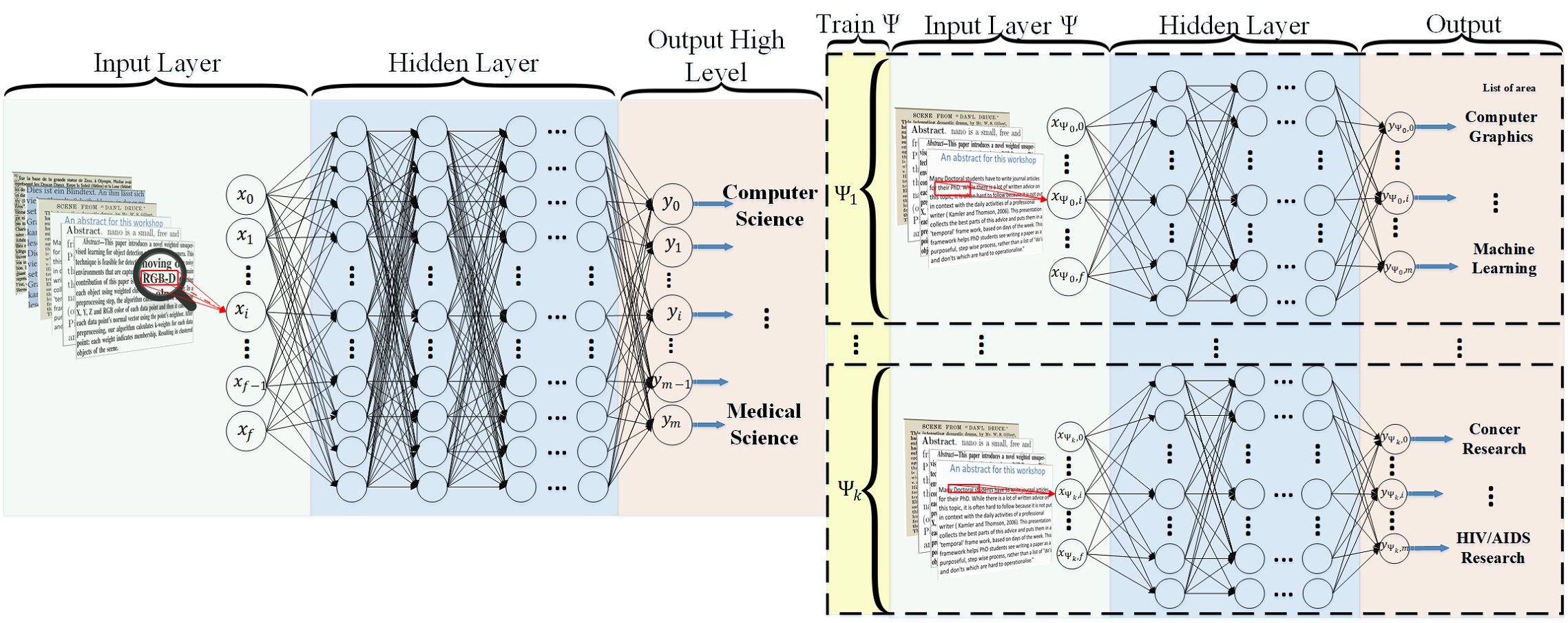
Quels algorithmes d’apprentissage automatique sont utilisés sur ces données ?
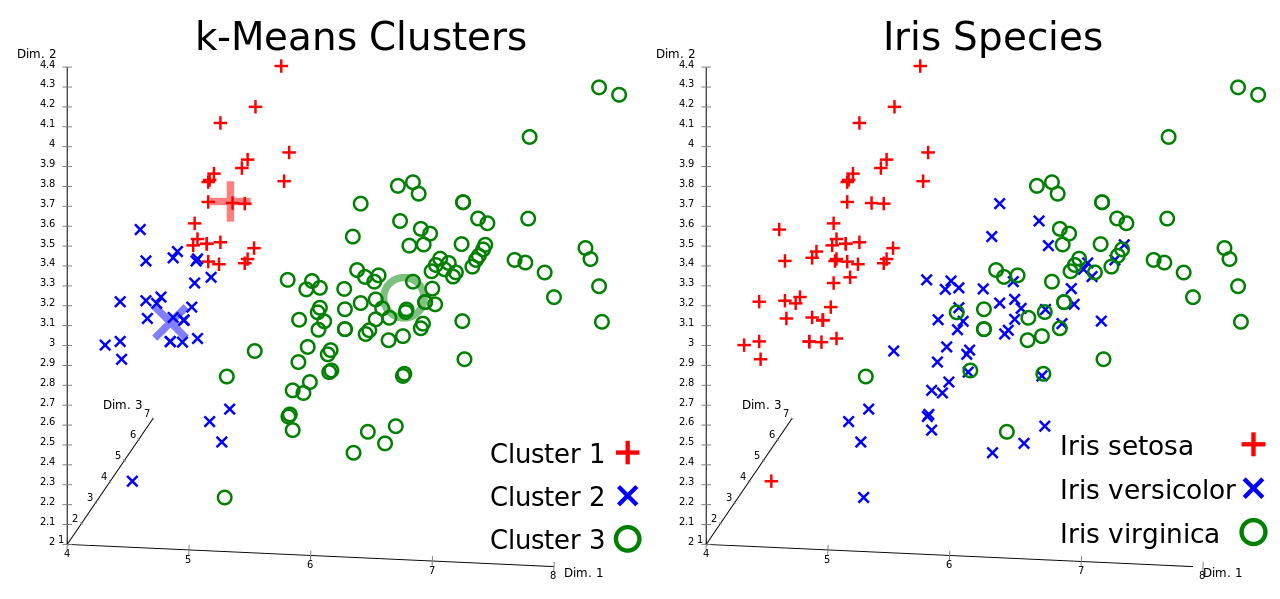
Regroupement (Clustering)
- Rassembler des individus en un nombre déterminé de groupes.
- Avantage: Permet de créer des étiquettes lorsqu’on n’a pas de variable réponse
- Inconvénient: Le nombre de groupes est choisi à l’avance
Modèles linéaires (GLM)
- Identifie une relation linéaire entre plusieurs caractéristiques et une variable réponse.
- Avantage: Tous les coefficient numériques peuvent être expliqués un par un.
- Inconvénient: Prend pour hypothèse que la relation est linéaire.
Arbres de décisions
- Crée un modèle de décision discret
- Prédire une variable réponse à partir de décisions
- Hiérarchique, facile à expliquer
 Source - Note: Les modèles de forêts aléatoires et de gradient boosting construisent plusieurs arbres pour obtenir davantage de précision. Ce sont des modèles très performants, mais difficiles à expliquer.
Source - Note: Les modèles de forêts aléatoires et de gradient boosting construisent plusieurs arbres pour obtenir davantage de précision. Ce sont des modèles très performants, mais difficiles à expliquer.
Réseaux de neurones
- Formés de composantes appelées neurones (modèles linéaires)
- Populaires pour l’apprentissage profond.
- Résultats très difficiles à expliquer (boîte noire)
- Permettent un très grand nombre de caractéristiques en entrée
Analyse de réseaux sociaux
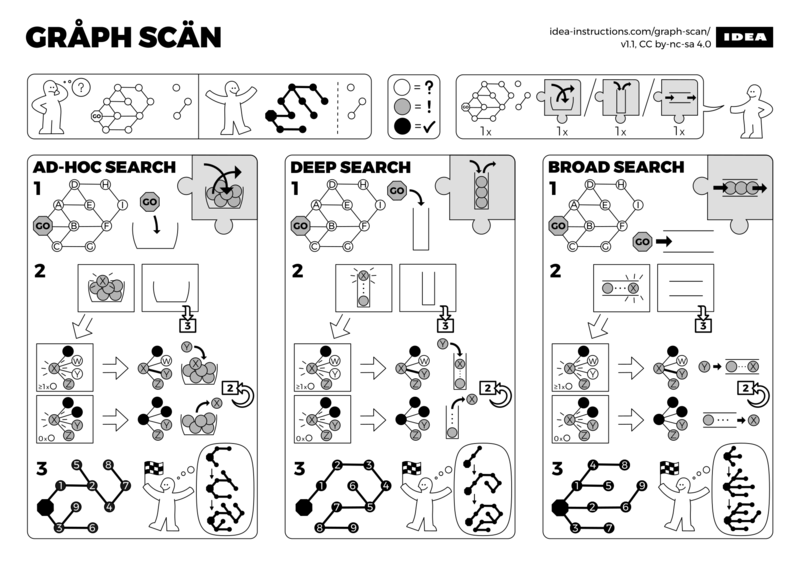
Traversée de graphes
Trouver le chemin le plus court répondant à une ou plusieurs contraintes.
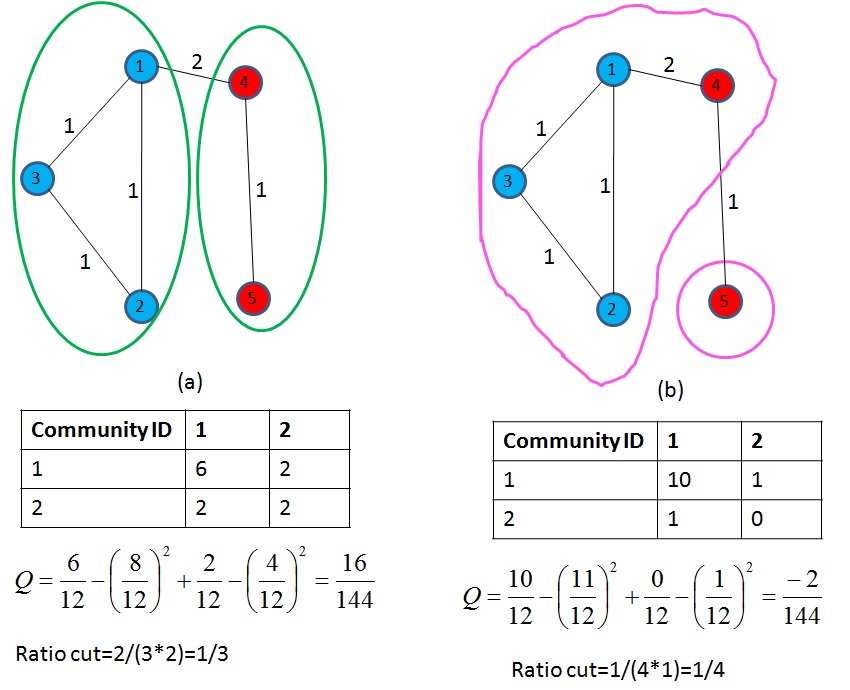
Segmentation de graphes
Systèmes de recommendation
Filtrage collaboratif
- Utiliser les opinions et évaluations d’un groupe pour émettre des recommendations à un individu de ce groupe. (Terveen and Hill 2001)
Exemple: Easyrec 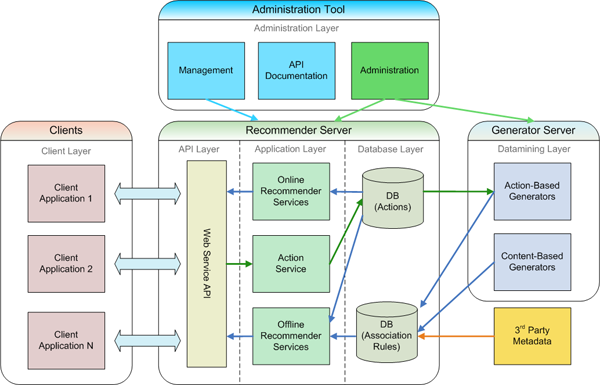 Source
Source
Quelles sont les limites actuelles des algorithmes d’apprentissage automatique ?
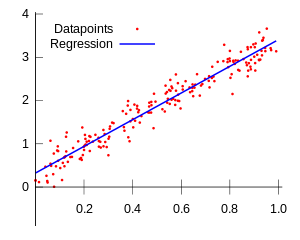
Quartet d’Anscombe
- Quatre ensemble de données (Anscombe 1973)
- Caractéristiques statistiques quasiment identiques
- En réalité très différents
- Illustre l’importance de l’exploration des données avant la modélisation
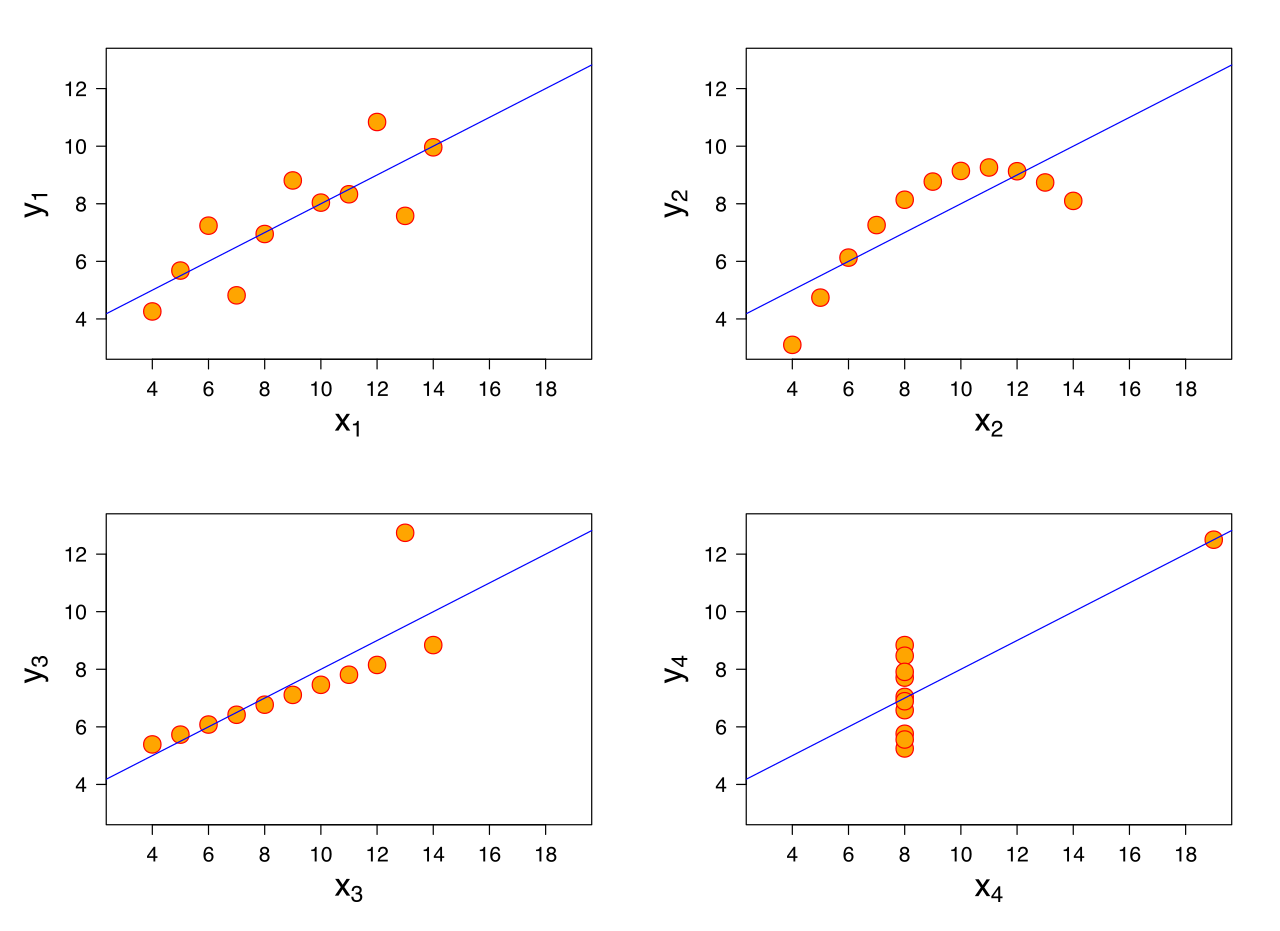 [Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Anscombe%27s_quartet]
[Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Anscombe%27s_quartet]
Le biais systémique et la discrimination
Il est de plus en plus facile de cacher la discrimination au travers d’algorithmes. Il suffit d’entraîner l’algorithme sur des données basées sur des décisions passées pour y inclure tous les biais des personnes qui ont prises ces décisions.
Les données en arrière-plan
(Ribeiro, Singh, and Guestrin 2016)
Comment vos données sont réellement utilisées ? La bonne façon
Prévenir la fraude
- Détection d’anomalies
- Algorithmes rapides qui évoluent avec les nouveaux modèles de fraude: apprentissage machine et service web pour livrer les résultats lors de la transaction.
- Inconvénient: Les modèles doivent être simples.
Airbnb Engineering & Data Science: Architecting a Machine Learning System for Risk
- Enjeu chez AirBNB: Les valeurs réponses observées (Ground truth) ne sont pas exactes, ce qui biaise le modèle et n’identifie pas correctement la fraude potentielle.
- Leur conseil: Enregistrer toutes les transactions, si une nouvelle variable est identifiée comme vecteur de fraude potentielle, il y a un historique de disponible.
- Conséquence: AirBNB conserve sur une longue période l’ensemble de leurs données transactionnelles.
- Avantage: Ce sont des données issues d’une relation d’affaires.
Éducation: Parcours de l’étudiant
- Types de données recueillies
- Travaux, examens, notes
- Préférence et style d’apprentissage
- Inscriptions
- Échecs et reprises
- Enseignant
- Utilisations
- Modéliser la probabilité d’un échec ou d’un décrochage (D. Yang et al., n.d.)
- Suggérer du matériel personnalisé à l’étudiant > it uses clustering algorithms to categories the students according to their learning capacity, needs, style and preferences Référence: How Machine Learning is Making Learning Interactive?
Éducation: Adapter la pratique de l’enseignant
- Aide à la résolution de problèmes
Much of our current educational system can be described as “memorize, regurgitate, and forget.” Students learn to “study for the test. […] Computers are very good in storage, retention, and regurgitation.”
Le futur de l’éducation
- L’humain ne peut plus compétitionner l’ordinateur pour plusieurs tâches
- Nouveaux modes d’enseignement: ce qui différencie l’humain
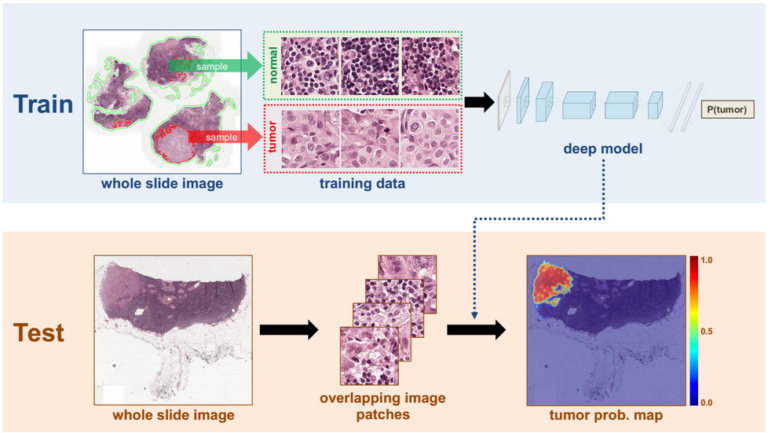
Soins de santé
Les algorithmes d’apprentissage profond peuvent identifier des tumeurs cancéreuses dans l’imagerie médicale.
Ex: Meilleure détection du cancer du sein
Enjeu: il faut le consentement du patient pour partager les images.
Entretien préventif
- Manufacture: bris d’équipement
- Services publics: électricité, aqueduc, voirie. Exemple: (Garcia, Sanz-Bobi, and Pico 2006; L. Zhang et al. 2016)
- Énergie: oléoducs et gazoducs (El-Abbasy et al. 2014)
- Services publics: usage par les citoyens
Comment vos données sont réellement utilisées ? La mauvaise façon
Weapons of math destruction
Weapons of math destruction, which O’Neil refers to throughout the book as WMDs, are mathematical models or algorithms that claim to quantify important traits: teacher quality, recidivism risk, creditworthiness but have harmful outcomes and often reinforce inequality, keeping the poor poor and the rich rich. They have three things in common: opacity, scale, and damage. They are often proprietary or otherwise shielded from prying eyes, so they have the effect of being a black box. They affect large numbers of people, increasing the chances that they get it wrong for some of them. And they have a negative effect on people, perhaps by encoding racism or other biases into an algorithm or enabling predatory companies to advertise selectively to vulnerable people, or even by causing a global financial crisis. Review: Weapons of Math Destruction
La bulle de confort
Systèmes de recommendations:
- Vont limiter la curiosité et l’exploration en maximisant la probabilité que le prochain choix de l’algorithme soit apprécié. Ex: Amazon, Netflix
- Solution potentielle: tenir compte de la cusiosité et de la diversité dans l’algorithme Poster (Menk dos Santos 2015)
- Vont éviter de choquer l’utilisateur avec des opinions divergentes des siennes. Ex: Facebook (Nguyen et al. 2014)
Segmentation de graphe:
- Les réseaux sociaux vont utiliser cette technique pour limiter les interactions dans un sous-graphe.
- Ex: Malgré des milliers d’abonnements Facebook ou Twitter, on voit toujours des publications des mêmes comptes.
La surveillance de masse
Les gouvernements utilisent le prétexte de la détection de nouveaux modèles de criminalité pour demander de plus en plus de données sur l’usage des moyens de communications par les citoyens.
the future-orientation increasingly severs surveillance from history and memory and the quest for pattern-discovery is used to justify unprecedented access to data
(Lyon 2014)
The NYPD is notorious for its intransigence on open records requests from the press and the public, particularly concerning documentation about the department’s extensive use of surveillance technology. In recent years, lawsuits have been filed to disclose information about the department’s network of surveillance cameras, its use of X-ray scanners in public, and the deployment of facial recognition technology
Transparency Advocates Win Release of NYPD “Predictive Policing” Documents
La prédiction des récidivistes
- Le modèle le plus utilisé (COMPAS) est secret, propriété de l’entreprise Northpointe, et n’est précis qu’à 60%
- Le modèle a un fort biais ethnique
Les Fake News
- Le combat contre la “fausse actualité” pourrait glisser facilement vers la censure.
- En particulier si les données d’entraînements sont étiquetées de façon subjective avec:
- des listes de sites de contenus absolument faux
- La nomination de sites de confiance absolue (Snopes, PolitiFact).
Modern machine learning for natural language processing is able to do things like translate from one language to another, because everything it needs to know is in the sentence its processing - Ian Goodfellow, OpenAI
- Peut-on vraiment faire confiance à Facebook pour régler le problème des “Fake news”? Facebook’s Latest Fix for Fake News: Ask Users What They Trust
References
Angles, Renzo, and Claudio Gutierrez. 2008. “Survey of Graph Database Models.” ACM Computing Surveys (CSUR) 40 (1). ACM: 1.
Anscombe, F. J. 1973. “Graphs in Statistical Analysis.” The American Statistician 27 (1). Taylor & Francis: 17–21. doi:10.1080/00031305.1973.10478966.
Chang, Fay, Jeffrey Dean, Sanjay Ghemawat, Wilson C Hsieh, Deborah A Wallach, Mike Burrows, Tushar Chandra, Andrew Fikes, and Robert E Gruber. 2008. “Bigtable: A Distributed Storage System for Structured Data.” ACM Transactions on Computer Systems (TOCS) 26 (2). ACM: 4.
El-Abbasy, Mohammed S, Ahmed Senouci, Tarek Zayed, Farid Mirahadi, and Laya Parvizsedghy. 2014. “Artificial Neural Network Models for Predicting Condition of Offshore Oil and Gas Pipelines.” Automation in Construction 45. Elsevier: 50–65.
Garcia, Mari Cruz, Miguel A Sanz-Bobi, and Javier del Pico. 2006. “SIMAP: Intelligent System for Predictive Maintenance: Application to the Health Condition Monitoring of a Windturbine Gearbox.” Computers in Industry 57 (6). Elsevier: 552–68.
Han, Jing, E Haihong, Guan Le, and Jian Du. 2011. “Survey on Nosql Database.” In Pervasive Computing and Applications (Icpca), 2011 6th International Conference on, 363–66. IEEE.
Lyon, David. 2014. “Surveillance, Snowden, and Big Data: Capacities, Consequences, Critique.” Big Data & Society 1 (2): 2053951714541861. doi:10.1177/2053951714541861.
Manning, Christopher, Mihai Surdeanu, John Bauer, Jenny Finkel, Steven Bethard, and David McClosky. 2014. “The Stanford Corenlp Natural Language Processing Toolkit.” In Proceedings of 52nd Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics: System Demonstrations, 55–60.
Menk dos Santos, Alan. 2015. “A Hybrid Recommendation System Based on Human Curiosity.” In Proceedings of the 9th Acm Conference on Recommender Systems, 367–70. ACM.
Moniruzzaman, ABM, and Syed Akhter Hossain. 2013. “Nosql Database: New Era of Databases for Big Data Analytics-Classification, Characteristics and Comparison.” arXiv Preprint arXiv:1307.0191.
Nguyen, Tien T, Pik-Mai Hui, F Maxwell Harper, Loren Terveen, and Joseph A Konstan. 2014. “Exploring the Filter Bubble: The Effect of Using Recommender Systems on Content Diversity.” In Proceedings of the 23rd International Conference on World Wide Web, 677–86. ACM.
Ribeiro, Marco Tulio, Sameer Singh, and Carlos Guestrin. 2016. “Why Should I Trust You?: Explaining the Predictions of Any Classifier.” In Proceedings of the 22nd Acm Sigkdd International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, 1135–44. ACM.
Sivic, Josef, and Andrew Zisserman. 2009. “Efficient Visual Search of Videos Cast as Text Retrieval.” IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence 31 (4). IEEE: 591–606.
Terveen, Loren, and Will Hill. 2001. “Beyond Recommender Systems: Helping People Help Each Other.” HCI in the New Millennium 1 (2001). Addison-Wesley, Reading, MA: 487–509.
Vinyals, Oriol, Alexander Toshev, Samy Bengio, and Dumitru Erhan. 2017. “Show and Tell: Lessons Learned from the 2015 Mscoco Image Captioning Challenge.” IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence 39 (4). IEEE: 652–63.
Yang, Diyi, Tanmay Sinha, David Adamson, and Carolyn Penstein Rosé. n.d. “Turn on, Tune in, Drop Out: Anticipating Student Dropouts in Massive Open Online Courses.” In.
Zhang, Lei, Fan Yang, Yimin Daniel Zhang, and Ying Julie Zhu. 2016. “Road Crack Detection Using Deep Convolutional Neural Network.” In Image Processing (Icip), 2016 Ieee International Conference on, 3708–12. IEEE.